Glossary of Paper and Printing Terminology
- Abrasiveness
- The level wear, resulting from friction, that paper, ink and coatings
cause on dies, cutting blades, plates, etc.
- The level wear, resulting from friction, that paper, ink and coatings
- Adhesive
- Cold Temperature (Cold Seal) Adhesive that will create a bond when
applied to a cold surface in a cold environment.
- Cold Temperature (Cold Seal) Adhesive that will create a bond when
- Adhesive Pressure Sensitive (Peel & Seal)
- It is called pressure sensitive because when the adhesive comes in
contact with a surface and pressure is applied to the label, the
adhesive will allow the face-stock to stick.
- It is called pressure sensitive because when the adhesive comes in
- Basis Weight
- The weight in pounds per ream (500 sheets) in the basic size for a
specific grade of paper.
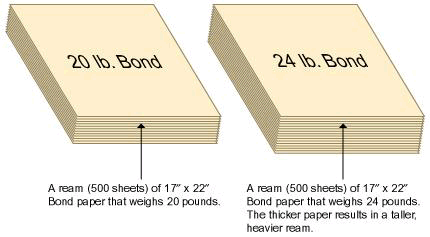
- The weight in pounds per ream (500 sheets) in the basic size for a
- Beater Dyed
- a type of paper that is dyed in the manufacturing process when the
material is still a slurry, resulting in a paper that is a solid color
all the way through the paper (if cut or ripped, the inside of the sheet
or fiber is colored the same as the outside).
- a type of paper that is dyed in the manufacturing process when the
- Bleed Through
- When printing from one side of the sheet is visible on the other side
due to ink problems opposed to show through where the problem results
from lack of opacity in the paper.
- When printing from one side of the sheet is visible on the other side
- Broke
- Machine trim or undesirable paper that is returned to the beaters.
- Bursting Strength
- The amount of uniform pressure required to pull a sheet of paper apart.
- Calendering
- A general term meaning pressing with a roll. The last operation on the
drying machine before the paper is wound on reels. Machine calenders are
stacks of vertical cast steel rolls that have polished ground surfaces.
The paper enters the stack at the top and is compacted and smoothed
progressively as it travels down the stack.
- A general term meaning pressing with a roll. The last operation on the
- Close Register
- When two colors fit tightly together with little or no trap allowance.
This requires precise alignment when printing.
- When two colors fit tightly together with little or no trap allowance.
- Die Cutting
- The main method or standard means of die cutting involves the use of
metal dies to give paper or substrate products specific shapes or
designs that cannot be accomplished by a straight cut on a web press or
a guillotine cutter.
- The main method or standard means of die cutting involves the use of
- Flat Bag
- A bag that has no side or bottom gussets.
- Flexography
- A printing process using a raised surface on a flexible plate, often
made of a rubberlike material, mounted on a rotary letterpress.
Flexographic inks are very thin, watery inks that dry very quickly.
- A printing process using a raised surface on a flexible plate, often
- Flooding
- Printing an entire sheet with ink or varnish.
- Foil Stamp (Hot Stamp)
- A printing process where a heated die is stamped onto a sheet of foil,
causing the foil to release from the backer onto the material being
printed.
- A printing process where a heated die is stamped onto a sheet of foil,
- Font
- A complete set of upper and lower case characters, numerials,
punctuation marks, and symbols of one specific typeface, size, and
style.

- A complete set of upper and lower case characters, numerials,
- Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)
- An independent, international, environmentally and socially oriented
forest certification organization. It trains, accredits and monitors
third-party certifiers around the world and works to establish
international forest management standards.
- An independent, international, environmentally and socially oriented
- Full Bleed
- Printing that goes to the edge of all four sides of the page.
- Glassine
- Translucent, smooth, grease-resistant paper made from highly beaten
chemical pulps, subsequently super-calendered.
- Translucent, smooth, grease-resistant paper made from highly beaten
- Halftone Screen
- A transparent material consisting of evenly spaced lines that is placed
between a photograph and the film to be exposed. The number of lines to
the inch controls the coarseness of the final dot formation; the more
lines used, the higher the quality. The screen that is used depends on
the paper and the type of printing process used. In electronic systems,
the screen is simulated by software.

- A transparent material consisting of evenly spaced lines that is placed
- Hard Copy
- The printed output of an image that is displayed on a monitor. It may be
output on paper or film.
- The printed output of an image that is displayed on a monitor. It may be
- Hickey
- A spot on a printed sheet that appears as a small white circle with ink
in the center, caused by particles such as dirt, dust, or bits of paper.
- A spot on a printed sheet that appears as a small white circle with ink
- Hot Stamping
- A printing process where a heated die is stamped onto a sheet of foil,
causing the foil to release from the backer onto the material being
printed.
- A printing process where a heated die is stamped onto a sheet of foil,
- Hot-Melt
- Adhesive A solid thermoplastic material that liquefies when heated and
then when it cools it re-solidifies to form a bond.
- Adhesive A solid thermoplastic material that liquefies when heated and
- Ink Holdout
- The ability of the paper to keep ink from absorbing into it.
- Knockout
- An opening, left in a printed area, in which a figure or photograph may
be placed. Reversing type or art out of the background so that when the
type or art is printed in that area it will not interfere with the color
you are trying to achieve.
- An opening, left in a printed area, in which a figure or photograph may
- Kraft Paper
- A sturdy brown paper with a high-pulp content used for wrapping paper,
grocery bags, and some varieties of envelopes.
- A sturdy brown paper with a high-pulp content used for wrapping paper,
- Kraft Process
- A chemical pulping process that cooks down the tree to remove lignin,
retaining the fibers for paper making.
- A chemical pulping process that cooks down the tree to remove lignin,
- Line Art
- In traditional graphic arts, line art refers to pictures that use no
halftones techniques and no mid-tones, just black and white. Also called
line copy.
- In traditional graphic arts, line art refers to pictures that use no
- Liner-board
- Kraft paperboard, generally unbleached, used to line or face corrugated
core board (on both sides) to form shipping boxes and various other
containers.
- Kraft paperboard, generally unbleached, used to line or face corrugated
- M (Unit of measure)
- Abbreviation for a quantity of 1000 units.
- Machine Direction
- The direction parallel to the forward movement of material through the
press.
- The direction parallel to the forward movement of material through the
- Machine Finish (MF)
- Finish that is obtained while the paper is on the paper machine.
Different finishes are obtained by the number of times the paper is
passed through rollers, either dry or wet.
- Finish that is obtained while the paper is on the paper machine.
- Machine Glaze (MG)
- Known as MG papers, these are paper that appear to have a glazed finish
on one side and a rough finish on another. Process occurs on a Yankee
dryer when wet paper comes into contact with a steam-heated, smooth
roller. Pressure is applied by the roller to the paper.
- Known as MG papers, these are paper that appear to have a glazed finish
- Mis-register
- A problem in multiple color printing when the different color images do
not line up properly as the successive colors are printed on the page.
- A problem in multiple color printing when the different color images do
- Mixed Office Waste
- Wastepaper generated from offices, such as letters, memos, invoices,
etc. which are collected and sorted for paper qualities.
- Wastepaper generated from offices, such as letters, memos, invoices,
- Moisture Resistance
- The ability of a material to resist taking on moisture and breaking down
when exposed to it.
- The ability of a material to resist taking on moisture and breaking down
- Mullen Test
- A test used to measure the bursting strength of paper. Also referred to
as pop test.
- A test used to measure the bursting strength of paper. Also referred to
- Negative
- A photographic image on film which reverses the black and white areas of
the original. The black areas on the original are clear on the negative
and the white areas of the original are black on the negative. The
negative film is used in the platemaking process.
- A photographic image on film which reverses the black and white areas of
- Negative Image
- A reversed image where the image that is usually black on a white
background is reversed to be white on a black background.
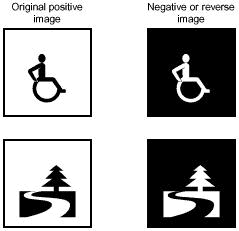
- A reversed image where the image that is usually black on a white
- Non-Image
- Area Any area, on an art-board, negative or plate, that is not to have
any printing.
- Area Any area, on an art-board, negative or plate, that is not to have
- Opacity
- The amount of “show through” in a sheet from one side to the other. The
higher the opacity the less likely that the printing on one side will be
visible from the other side.
- The amount of “show through” in a sheet from one side to the other. The
- Out-of-Register
- When an image is not printing in the exact location that it is suppose
to. When printing more than one color, if the colors do not line up
properly, they are out of register.
- When an image is not printing in the exact location that it is suppose
- Pantone Matching System (PMS)©
- A registered name for an ink color matching system used to compare,
match and identify specific colors.

- A registered name for an ink color matching system used to compare,
- Paper Grade
- The quality of paper as determined by the ingredients of the stock such
as wood or cotton fiber and the method of manufacturing. All papers fit
into a group or type of paper which is its grade.
- The quality of paper as determined by the ingredients of the stock such
- Post-Consumer Waste
- Waste paper that has passed through the enduser, such as newspapers,
office papers, paper bags and cartons.
- Waste paper that has passed through the enduser, such as newspapers,
- Post-Printed Bags
- Any bag that is printed or hot stamped after the bag has been
manufactured. Allows for small quantities to be printed with faster lead
times.
- Any bag that is printed or hot stamped after the bag has been
- Pre-Consumer Waste
- Waste paper that has been disposed of during the converting process.
This may consist of paper trim, die clippings from die cutting of
envelopes and corrugated boxes, or waste off the printing press. This is
waste that has not passed through the end user.
- Waste paper that has been disposed of during the converting process.
- Pre-flight
- A procedure used to be sure all digital files have been prepared
properly before putting them into production. They are checked for
correct type fonts, completeness, composition, and compatibility.
- A procedure used to be sure all digital files have been prepared
- Proof
- A copy of the artwork representing the finished product. It is used for
review and approval.
- A copy of the artwork representing the finished product. It is used for
- Raster Image
- Also called bitmap image, is a reproduced graphic (text or image) which
is displayed on a video monitor as pixels or on paper as an array of
dots. It is identified in terms of resolution, such as dots per inch or
pixels per inch. Raster images are produced by scanners, digital cameras
or software editing programs.

- Also called bitmap image, is a reproduced graphic (text or image) which
- Raster Image File Format (RIFF)
- An expanded version of the TIFF file format used for graphics, which is
used by many scanners.
- An expanded version of the TIFF file format used for graphics, which is
- Register
-
- Aligning the images of each color so that they are printed in the
proper location on the paper. - Aligning one part of a form with the next so that all parts are
aligned. All parts must be in register so that when the form
isimprinted or filled out, the impression will transfer to the
proper location on each part.
- Aligning the images of each color so that they are printed in the
-
- Release Liner (Peel & Seal)
- The backer material or carrier sheet of a pressure sensitive material.
It protects the adhesive until time of use. Generally has a release
coating applied to allow the adhesive to release easily. Also referred
to as the backing or liner.

- The backer material or carrier sheet of a pressure sensitive material.
- Repeat Length
- On a web press, it is the circumference of the impression cylinder.
- Resolution
- The measurement of output quality expressed in pixels (dots) per inch on
a computer monitor or dots per inch on printed media. For example, a
monitor displaying a resolution of 800 by 600 refers to a screen capable
of displaying 800 pixels in each of 600 lines, which translates into a
total of 480,000 pixels displayed on the screen. When referring to
printed media, a 300 dpi (dots per inch) printer for example, is capable
of outputting 300 dots in a one-inch line, which means that it has the
ability of printing 90,000 distinct dots per square inch (300 x 300).
- The measurement of output quality expressed in pixels (dots) per inch on
- Reverse
- To produce an image that is white on a solid background. When printing,
the reverse area will be the color of the stock being printed on.

- To produce an image that is white on a solid background. When printing,
- Reverse Type
- The background is printed instead of the type. The type will be the
color of the stock being printed on.

- The background is printed instead of the type. The type will be the
- Rub-Off
-
- Ink on printed sheets, after sufficient drying, which smears or
comes off on the fingers when handled. - Ink that comes off the cover during shipment and transfers to other
covers or to the shipping carton or mailer; also called Scuffing.
- Ink on printed sheets, after sufficient drying, which smears or
-
- Sans Serif Type
- A typeface without serifs, the cross strokes on the ends of the letters.

- A typeface without serifs, the cross strokes on the ends of the letters.
- Screen Printing
- A printing method where a squeegee is used to force ink through a mesh
fabric that has a stenciled image area that allows the ink to pass
through the mesh to create the image.
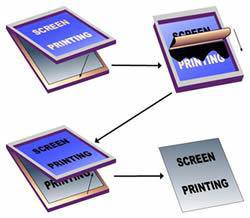
- A printing method where a squeegee is used to force ink through a mesh
- Screen Tint
- A screen pattern that consists of dots that are all the same size and
create an even tone.

- A screen pattern that consists of dots that are all the same size and
- Serif Type
- A typeface that has the cross strokes on the ends of the letters.

- A typeface that has the cross strokes on the ends of the letters.
- Single Wall Bag
- Manufactured from a single layer of paper.
- SOS Bag
- Self Opening Style. Four bag sides and the bottom, with no handle, and a
serrated-top edge. Generally know for use as lunch bags and grocery
style bags in a variety of sizes.
- Self Opening Style. Four bag sides and the bottom, with no handle, and a
- Soy Based Ink
- Inks whose pigment vehicles contain soybean oils instead of petroleum
products. Soybean inks are a good alternative to petroleum base inks
because of their ease of use and because of their environmental
considerations.- Periodically we are asked if our bags can be printed with soy inks.
Soy based inks have a very limited role in flexographic printing. We
only print flexographically. - Offset litho inks are thick and pasty. The materials within which
pigments are dispersed are petroleum based compounds. It is these
thick, pasty compounds that soy oil is designed to replace in offset
litho inks.
- Periodically we are asked if our bags can be printed with soy inks.
- Inks whose pigment vehicles contain soybean oils instead of petroleum
- Substrate
- The material or stock that serves as the base onto which another
material, chemical or solution is applied. Materials such as paper,
plastic, film and acetate can all be the base substrate that may have
ink, adhesive, photosensitive emulsion or a laminated material applied
to one or both sides.
- The material or stock that serves as the base onto which another
- Supercalendered
- An additional papermaking process where the paper runs through a set of
alternating steel and fiber covered rollers. Supercalendering produces a
very smooth thin sheet.
- An additional papermaking process where the paper runs through a set of
- Tack
- The stickiness of ink required to adhere properly to the type of
substrate being printed on. To much tack can cause the fibers to be
pulled off the paper causing picking.
- The stickiness of ink required to adhere properly to the type of
- Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
- A graphics file format developed by Aldus, Adobe, and Apple that is
especially suited for representing large bitmaps, such as scanned black
and white or color images.
- A graphics file format developed by Aldus, Adobe, and Apple that is
- Tear Strength
- Paper’s ability to resist tearing while going through various stages of
production such as printing, folding, book binding and miscellaneous
bindery operations.
- Paper’s ability to resist tearing while going through various stages of
- Tensile Strength
- The ability of the paper to withstand the stress and strain applied to
it before breaking down and pulling apart.
- The ability of the paper to withstand the stress and strain applied to
- Tint
-
- The addition of white to a color.
- Also, when printing a color in any type of screening that causes the
ink coverage to be less than 100%.
-
- Trapping
- The overlapping of adjoining colors or ink to help prevent the
possibility of a fine white area showing between colors due to
mis-registration of color negatives or due to normal variations on the
press.
- The overlapping of adjoining colors or ink to help prevent the
- Turn-top Bag (Folded top)
- A style of bag construction where the top of the bag is folded to the
inside yielding a more finished look than the “saw tooth” style.
- A style of bag construction where the top of the bag is folded to the
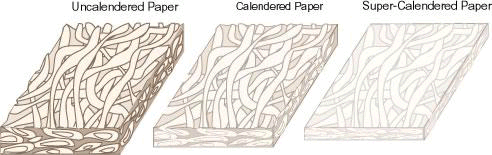
- Uncalendered
- Paper Paper that has not been sent through the stack of polished steel
rollers used in the calendering process which smooths the surface of the
paper.

- Paper Paper that has not been sent through the stack of polished steel
- Vector Graphics
- Graphics and pictures represented by lines and curves rather than using
dot or pixels as used on bitmapped or raster images. Vector graphics are
infinitely scalable without loss of quality.
- Graphics and pictures represented by lines and curves rather than using
- Virgin Paper
- Paper manufactured from new pulp. Does not contain any recycled
material.
- Paper manufactured from new pulp. Does not contain any recycled
- Wet-Strength
- Papers Once wet, ordinary papers lose most of their original
dry-strength properties. Wet strength papers possess properties that
resist disintegration and rupture when saturated with water. Papers are
classified wet strength when they retain 15% or more of their
dry-tensile strength. Superior quality wet strength papers may retain as
much as 50%.
- Papers Once wet, ordinary papers lose most of their original
